What Are Impacted Wisdom Teeth?
An impacted wisdom tooth is a third molar that fails to erupt fully or correctly into the mouth due to lack of space, improper angulation, or obstruction by other teeth or bone.
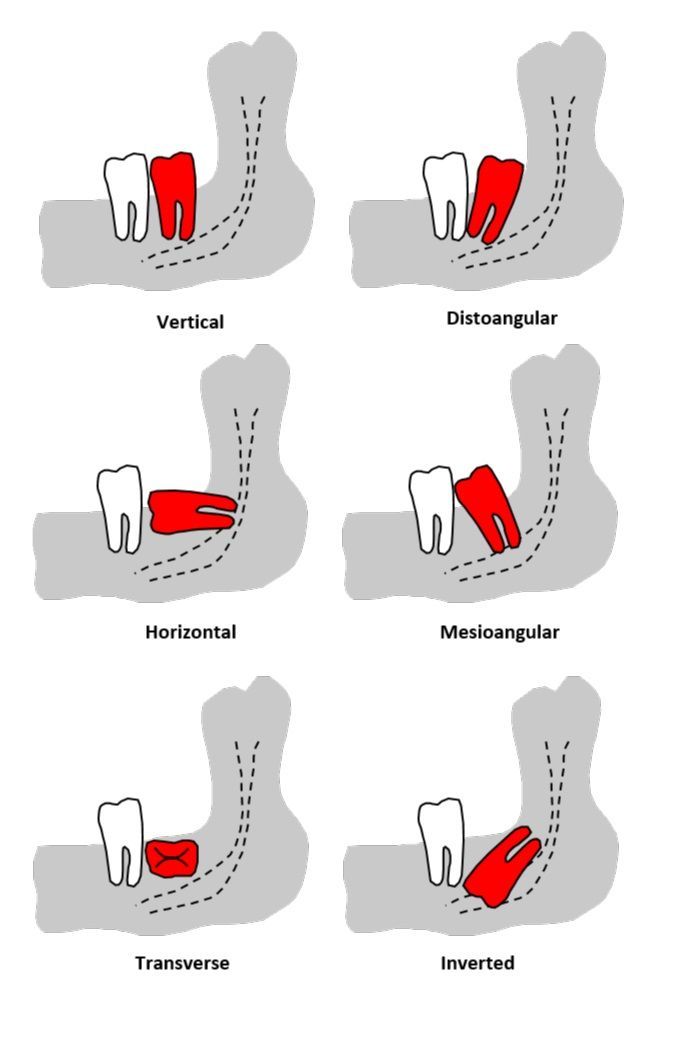
There are several types of impactions:
- Mesial impaction: tooth is angled forward toward the front of the mouth
- Distal impaction: angled toward the back of the mouth
- Vertical impaction: tooth is upright but doesn't break through the gum
- Horizontal impaction: tooth lies sideways within the jaw
What Causes Wisdom Teeth to Become Impacted?
The biggest reason: lack of space in the jaw. Human jaws have evolved to be smaller, and often there simply isn’t room for a third set of molars.
Other causes include:
- Genetic factors (jaw size, tooth size)
- Delayed or abnormal eruption patterns
- Overcrowding of adjacent teeth
Signs and Symptoms of impacted wisdom teeth
Some impacted wisdom teeth are asymptomatic, but many cause:
- Jaw pain or stiffness
- Swollen or bleeding gums
- Bad breath or bad taste
- Headaches or earaches
- Visible crowding or shifting of teeth
If infection sets in (pericoronitis), symptoms can become severe and may include fever and difficulty opening the mouth.
Risks of Leaving Impacted Wisdom Teeth Untreated
Impacted third molars can cause more than just discomfort. Over time, they can lead to:
1. Cyst Formation
- A fluid-filled sac can form around the tooth
follicular cyst, potentially damaging bone or adjacent roots
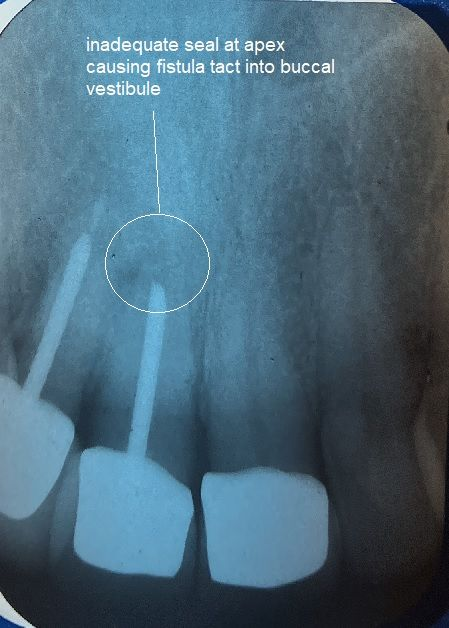
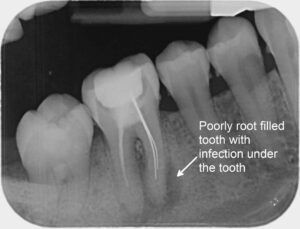
2. Infection
- Partially erupted teeth are a trap for food and bacteria, leading to
gum infections or abscesses. This is called
periconitis.
3. Damage to Adjacent Teeth
- Impacted teeth can push against nearby molars, causing
resorption, cavities, or shifting
4. Crowding and Bite Issues
- Wisdom teeth pressure can undo years of orthodontic work
5. Rare but Serious Tumors
- Wisdom teeth originate from ectoderm and ectomesenchyme, layers of embryonic tissue that form the tooth bud. If this tissue becomes trapped. Primal undifferentiated germ-layer tissues of the tooth bud have the potential (differentiate), benign or malignant growths.
When Should You Get Wisdom Teeth Removed?
Wisdom teeth be evaluated during the teen years. Early removal is often best because:
- The roots aren’t fully formed
- The bone is softer, allowing easier recovery
- There’s less risk of complications
Final Thoughts
Impacted wisdom teeth are common — and so are the problems they cause if left alone. If you're experiencing jaw pain, swelling, or crowding, it may be time to get them evaluated or removed.