A Tooth Abscess Uncovered: What You Need to Know
This is paragraph text. Click it or hit the Manage Text button to change the font, color, size, format, and more. To set up site-wide paragraph and title styles, go to Site Theme.
What Is a Tooth Abscess?
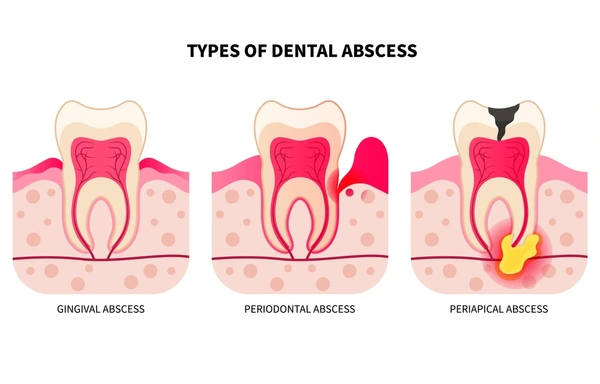
A tooth abscess—also known as a dental abscess—is a painful, pus-filled pocket that develops in your tooth, gums, or jawbone due to a bacterial infection. The most common varieties are:
- Periapical abscess: Forms at the root tip due to deep infection in the tooth pulp.
- Periodontal (gum) abscess: Affects the gums and supporting structures.
-
- Gingival abscess: Develops in the gum tissue alone.
What Causes a Tooth Abscess?
Primary causes include:
- Deep tooth decay that reaches the pulp
- Cracked or damaged teeth or fillings
- Advanced gum disease
- Prior root canal treatments that failed short fill or inadequate apical seal
Recognizing the Symptoms
A tooth abscess often makes its presence known through:
- Persistent, throbbing tooth pain—sharp, shooting, or radiating to jaw, ear, or neck
- Heightened sensitivity to hot, cold, or pressure
- Swollen gums or cheek, possible pus or gum “pimple” (gum boil)
- Foul taste or odor in the mouth
- Systemic effects like fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, fatigue, or nausea

Why Ignoring It Can Be Dangerous
When left untreated, a dental abscess can spiral into serious health threats—spreading to the jawbone, sinuses, bloodstream, or even the brain. In rare cases, it can lead to sepsis or life-threatening conditions.
Immediate Steps You Can Take at Home (Temporary Relief Only)
While home care cannot cure the abscess, these measures can ease your discomfort while you await treatment:
- Rinse with warm salt water to reduce swelling and bacteria
- Apply a cold compress to numb pain and lower swelling
- Avoid hot, cold, or chewy foods on the affected side
- Use OTC painkillers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen per the label instructions
Professional Dental Treatments That Work
Only a dentist can definitively treat a tooth abscess. Treatment options may include:
- Drainage and Cleaning: Removing pus and reducing pressure
- Root Canal Therapy: Removes infected pulp and seals the tooth
- Tooth Extraction: Reserved for teeth that cannot be saved
- Antibiotics: Prescribed when infection has spread or doesn’t resolve quickly
Preventing Future Abscesses
Strong oral hygiene and lifestyle habits are your best defense:
- Brush twice daily with fluoride paste and floss once daily
- Limit sugary and starchy snacks
- Attend routine dental exams with x-rays and cleanings twice a year
- Treat cavities, gum issues, and dental trauma promptly
The Bottom Line
A tooth abscess is more than a stubborn toothache—it’s an infection that can escalate into serious health issues if untreated. If you’re experiencing symptoms like persistent dental pain, swelling, or fever, don’t wait.
Contact us at Dentistriverviewfl.com immediately to get the care you need and protect your oral and overall health.









